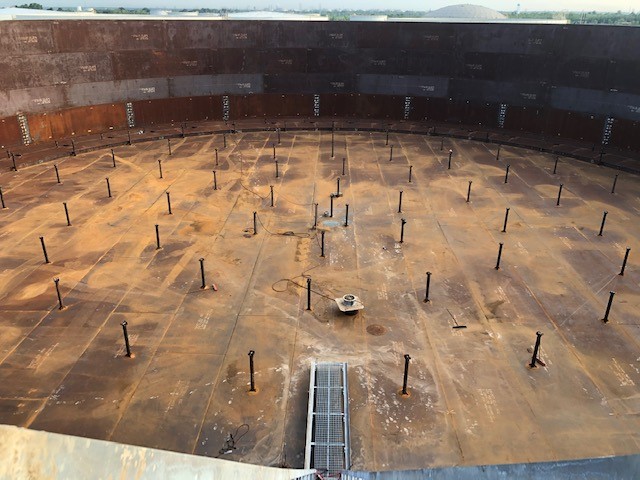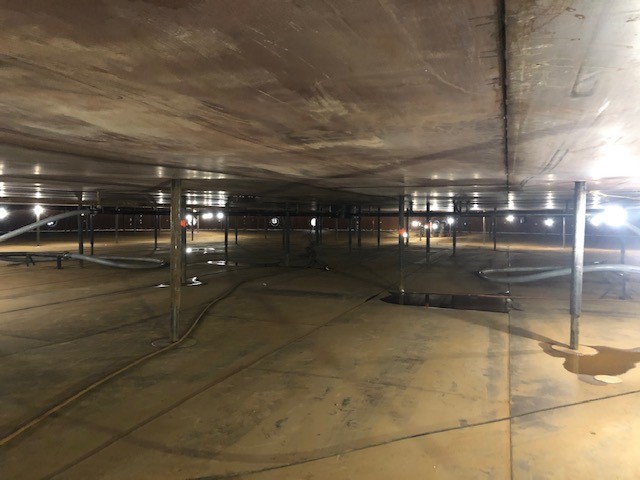
Aboveground Storage Tank Repair: When Is It Needed, and How Is It Done?
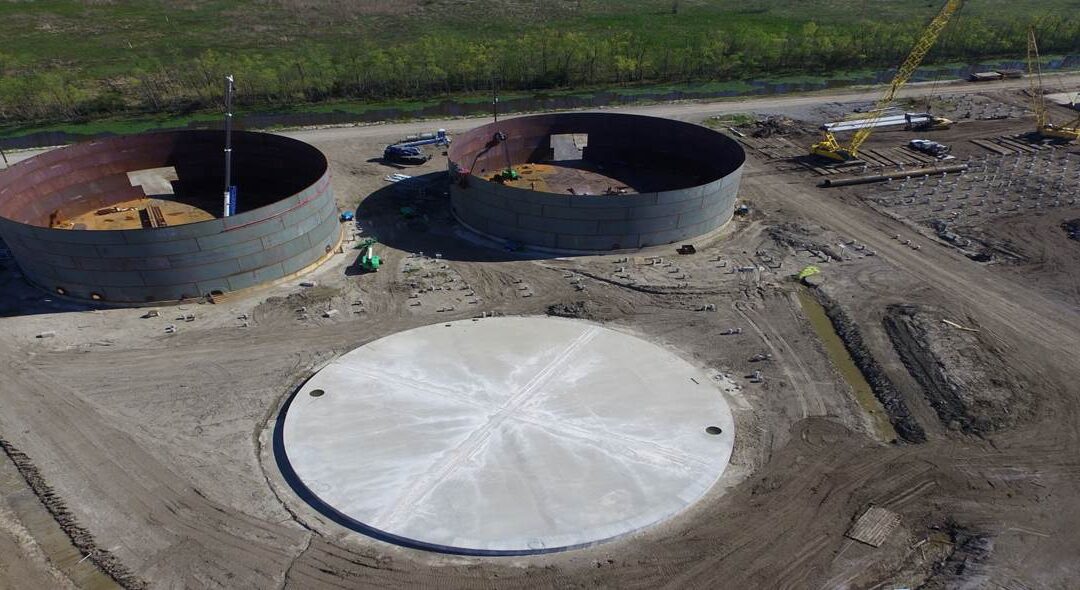
Aboveground storage tanks are built to be incredibly durable, safely storing hazardous liquids and gasses for decades. However, there’s always a chance yours may need to be repaired.
Let’s talk about how to know when your aboveground storage tank needs repair, as well as some methods in which those repairs can be executed.
How Long Do Aboveground Storage Tanks Last?
Aboveground storage tanks last an average of 20 years. However, this can vary tremendously based on factors like:
- Tank fabrication material
- Tank fabrication method
- Substance(s) stored in the tank
- Tank special features
- Tank location
- Tank size
- Tank maintenance protocols
If your aboveground storage tank is built and maintained well, it should last those full 20 years or more. But even the highest-quality, most well-maintained tanks require repairs at some point.
4 Signs That Your Aboveground Storage Tank Needs Repair
It’s important to identify when your aboveground storage tank needs repair as soon as possible. Letting damage or inefficiencies go unnoticed for too long can result in disastrous, unsafe conditions for your people and the environment.
If you recognize that your aboveground storage tank shows any of the following signs, you should contact a repair technician for a professional inspection promptly.
1. Your Aboveground Storage Tank’s Legs Are Unstable
If your aboveground storage tank’s legs are wobbling, it’s not properly supported. This is a major issue when you consider how much weight those legs need to support — between the tank itself and the materials within it. Improper support can cause the tank to collapse or fall over, spilling its contents all over the surrounding area.
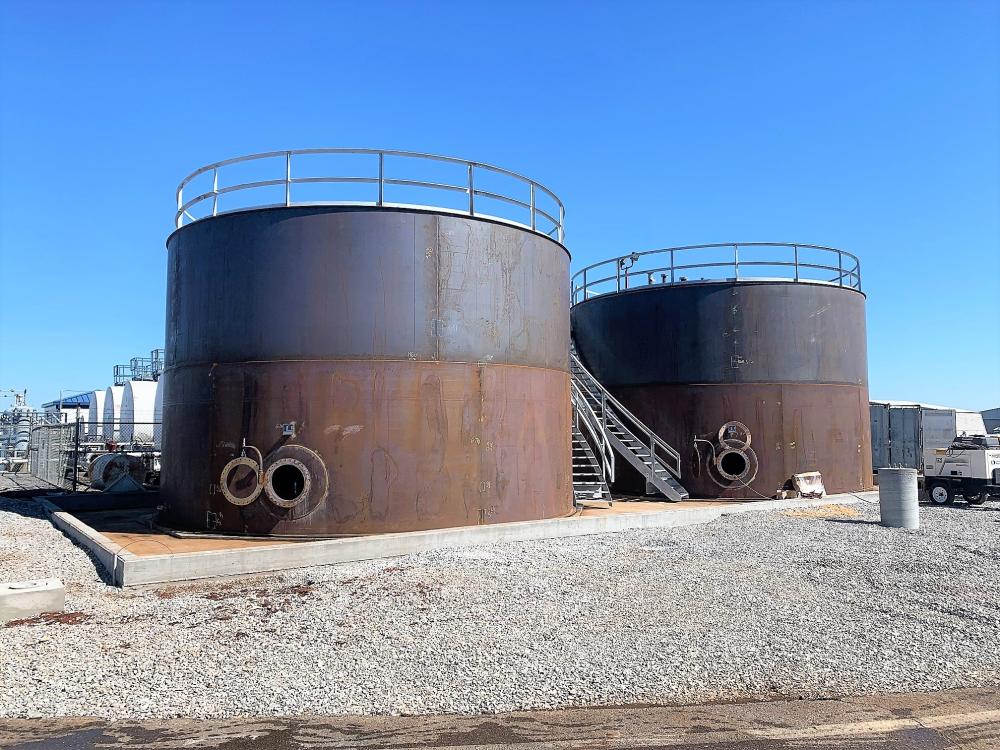
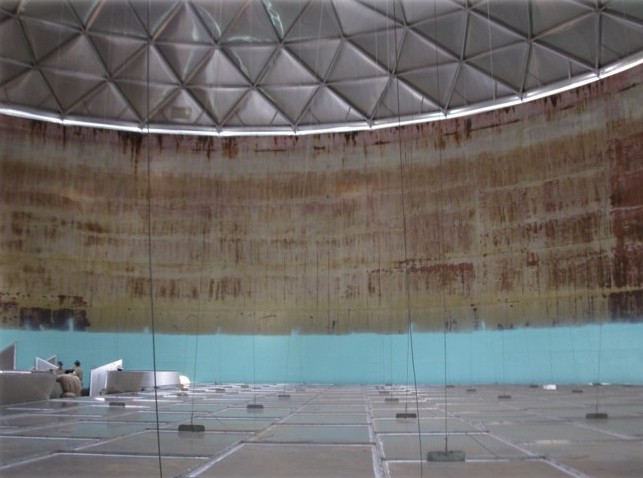
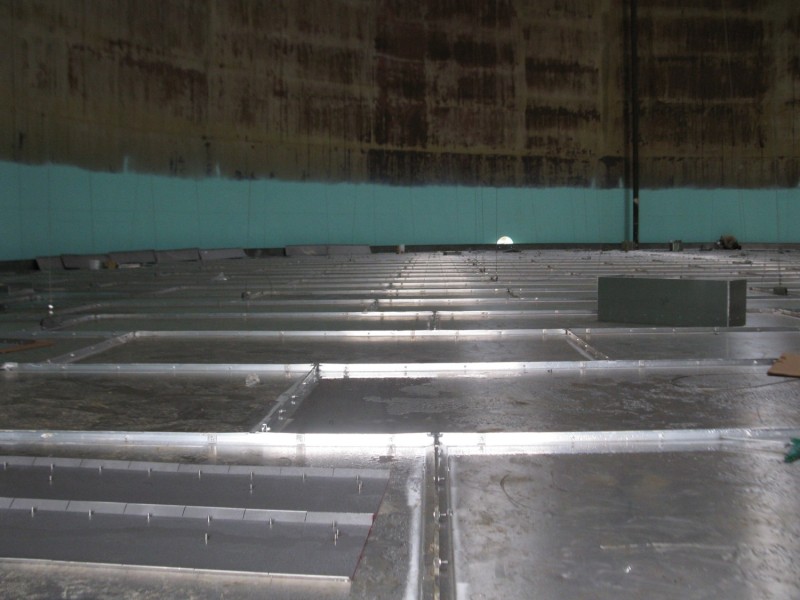
2. Your Aboveground Storage Tank’s Surface Is Deteriorating
You may be able to notice signs of tank deterioration by looking at it or by running your hand along its surface. The surface should be smooth and free of any bumps, dimples, divots, or rust.
If you do notice any imperfections in your tank’s surface, act immediately. Over time, those symptoms can worsen and turn into holes, which is an obvious problem.
3. Your Aboveground Storage Tank Is Leaking
Besides necessary vent lines, fill pipes, and exit pipes, your aboveground storage tank should be completely sealed. Make sure to check your tank’s surface, filters, and valves for a full inspection.
If you notice holes, drips, or leaks — even the smallest ones — your tank needs repair. A small drip today could be a full-blown spill tomorrow.
4. Your Aboveground Storage Tank Is Almost 20 Years Old
If your aboveground storage tank is approaching its 20-year average life expectancy, it’s a good idea to schedule an inspection — even if it’s not showing any of the signs mentioned above. When safety is a high priority, it’s important to be proactive.
Worst case scenario? You spent a few hours and a few hundred dollars to get peace of mind that your tank’s still functioning properly. Best case scenario? You find and fix an issue that wasn’t noticeable but could have caused hundreds of thousands of dollars in damage and severe personnel and environmental harm if left untreated.
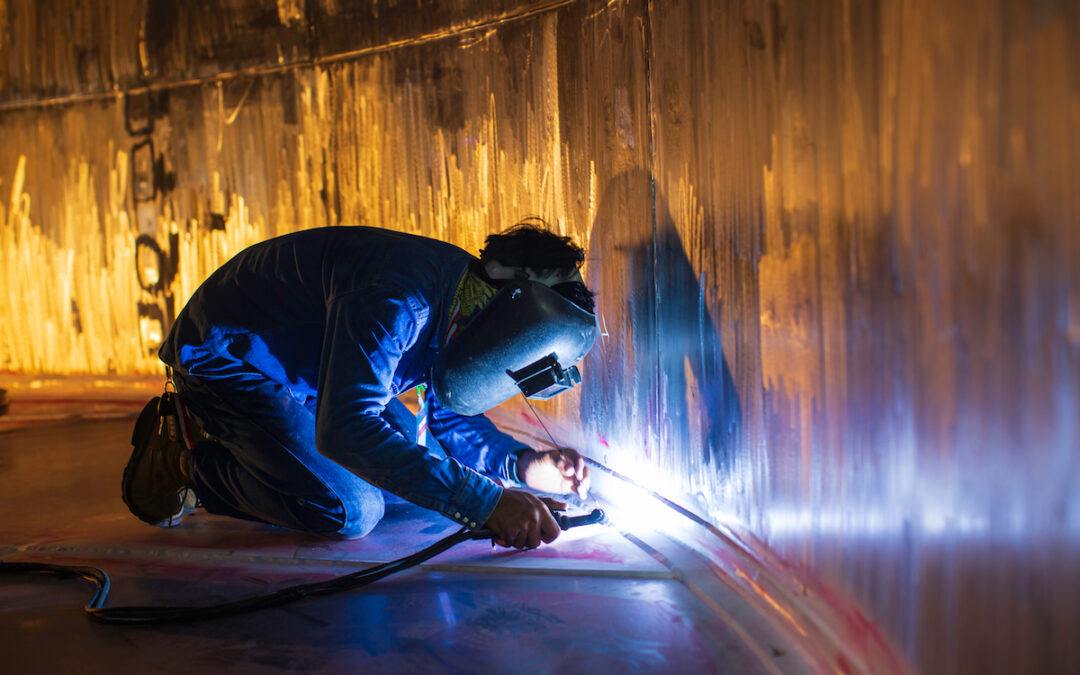
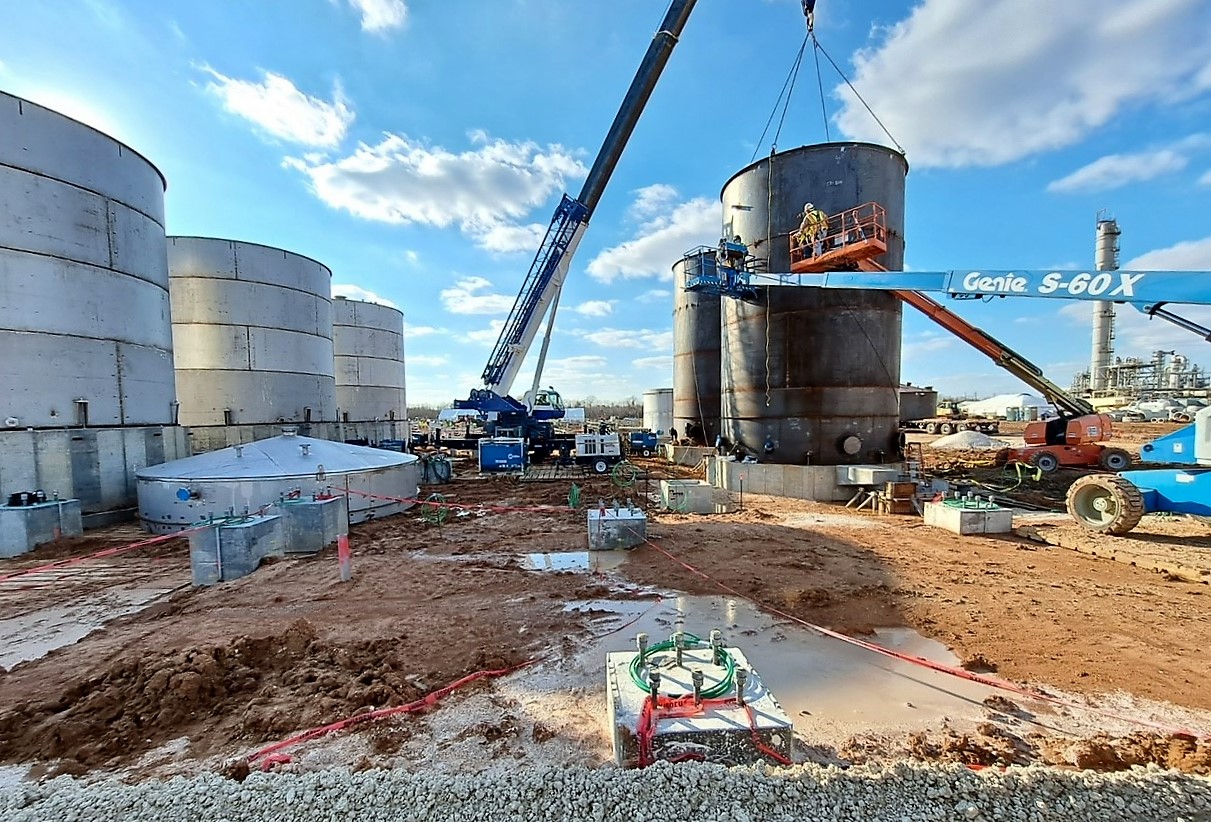
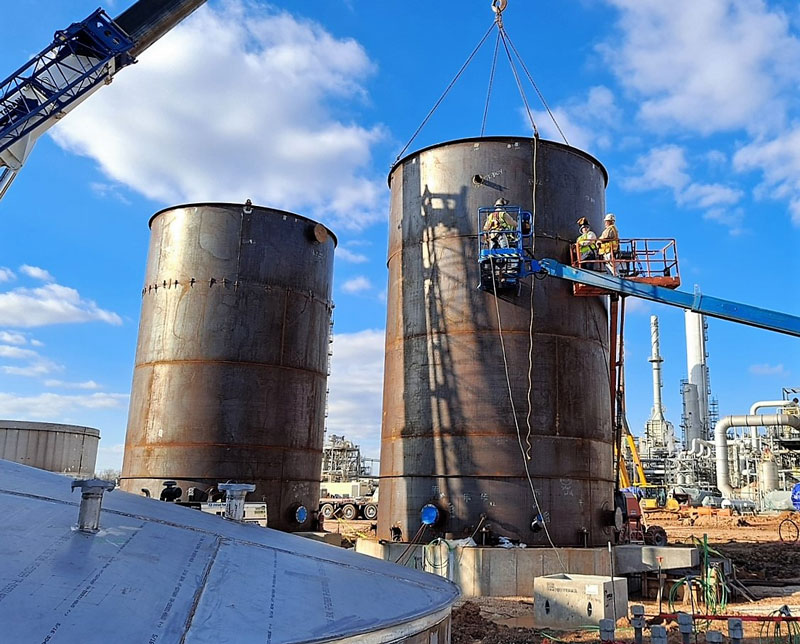
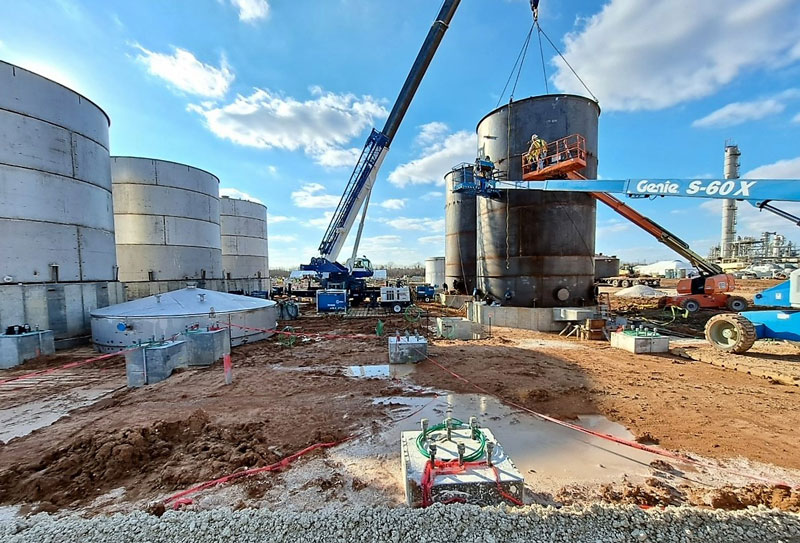
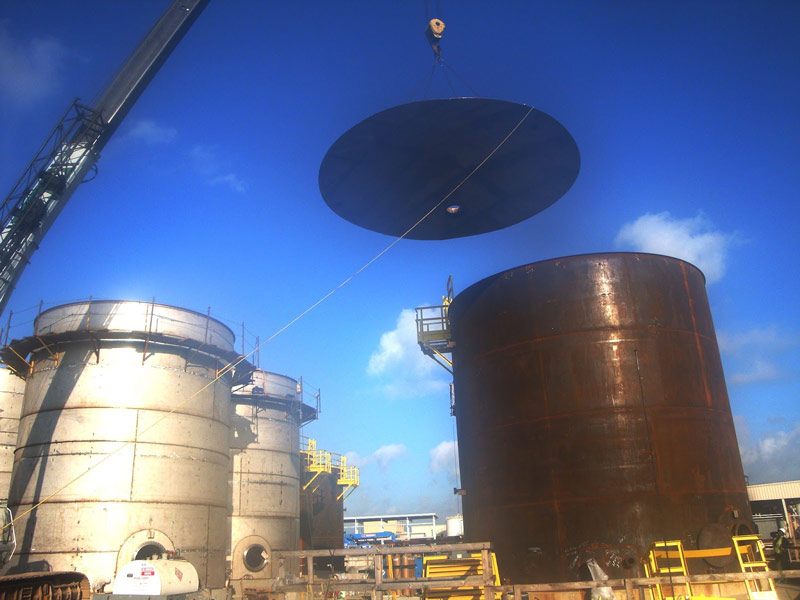
How to Repair Your Aboveground Storage Tank
There are various methods of aboveground storage tank repair. As long as they comply with API standards and regulations, they’re viable for use. Some common ones include:
- Welding replacement steel plates onto the tank
- Filling tanks with fiberglass and coating them in resin and fabric
- Repairing holes with laminating epoxy and epoxy putty
- Inserting new liners and grout
Many of the traditional aboveground storage tank repair methods listed above involve difficult, time-consuming work. That’s why it’s important to get the repairs done right on the first try.
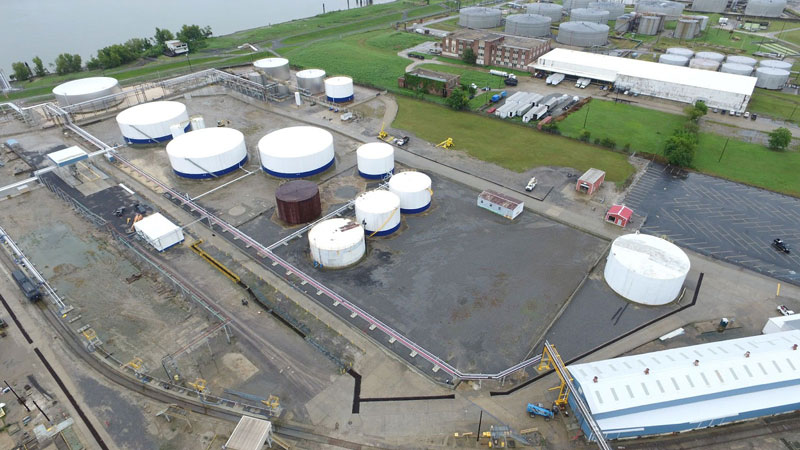
PALA’s 3D Laser Scanning Tank Services
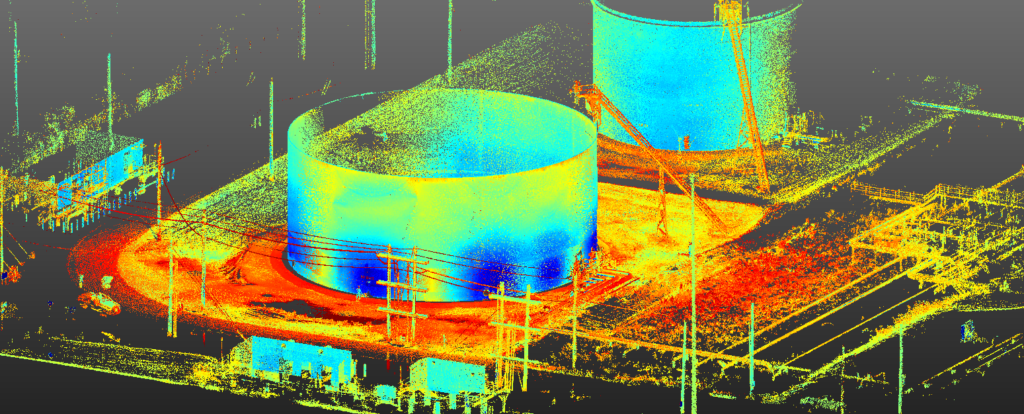
To ensure that aboveground storage tank repairs are done effectively and efficiently, PALA uses cutting-edge laser scanning technology from Novlum uniTank.
With this technology, we can conduct a comprehensive analysis and inspection within just a few hours, giving you real-time data to inform repair decisions. We can document existing tank conditions, perform fit-for-service studies, and use precise dimensional data for tank repairs, teardowns, and rebuilds.
It’s a fast, safe, and cost-effective option that sets the aboveground storage tank repair process up for success. Learn more about this 3D laser scanning technology and how it can benefit your application here.
Contact PALA For Your Aboveground Storage Tank Repair Needs
Aboveground storage tanks are durable, but they won’t last forever. If you notice something’s wrong with yours, it’s best to identify the problem and resolve it as quickly as possible. That’s what we’re here for.
PALA is your single source for comprehensive aboveground storage tank services. Using 3D laser scanning, we can ensure the safe storage of hazardous substances so you can keep your people, facility, and environment out of harm’s way. For more information on our aboveground storage tank repair capabilities, give our team a call or contact us online.














